1. Objective
To ensure proper risk assessment is carried out for all the Information and information processing assets at Integra. The procedure outlines the steps to be taken for conducting and assessing the risks associated with various assets including but not limited to process, equipment or people assets of Integra and provides a framework for mitigating them.
2. Scope
This is applicable to all Information covering risk identification, planning, and mitigation & tracking assets across the organization at Integra.
3. Reference
Standards: ISO 27001:2022 Information Security Management System
4. Definition
To identify all the elements of ISMS of Integra that has a business impact. At this point of time, the following elements (classification of information assets) have been identified as critical.
To define a risk assessment methodology for Integra and criteria for risk acceptance and acceptable level of risks based on applying appropriate business information security through appropriate selection of controls of ISO 27001:2022 international standards for ISMS and in line with Integra ISMS policies.
5. General Principles
5.1 Overview
Integra has performed a risk assessment exercise to ensure that the information security risks faced are comprehensively identified and to adopt appropriate risk management strategies for mitigation. This risk assessment shall consider business impact and consequences that may arise owing to loss of confidentiality, integrity and availability of information or information processing facilities.
The risk assessment shall consider the organization’s assets, viz., IT hardware and software, information on paper or in electronic format, personnel, office equipment’s, communication and utility services, etc.; the applicable threats to these assets and vulnerabilities that could be exploited to compromise these assets.
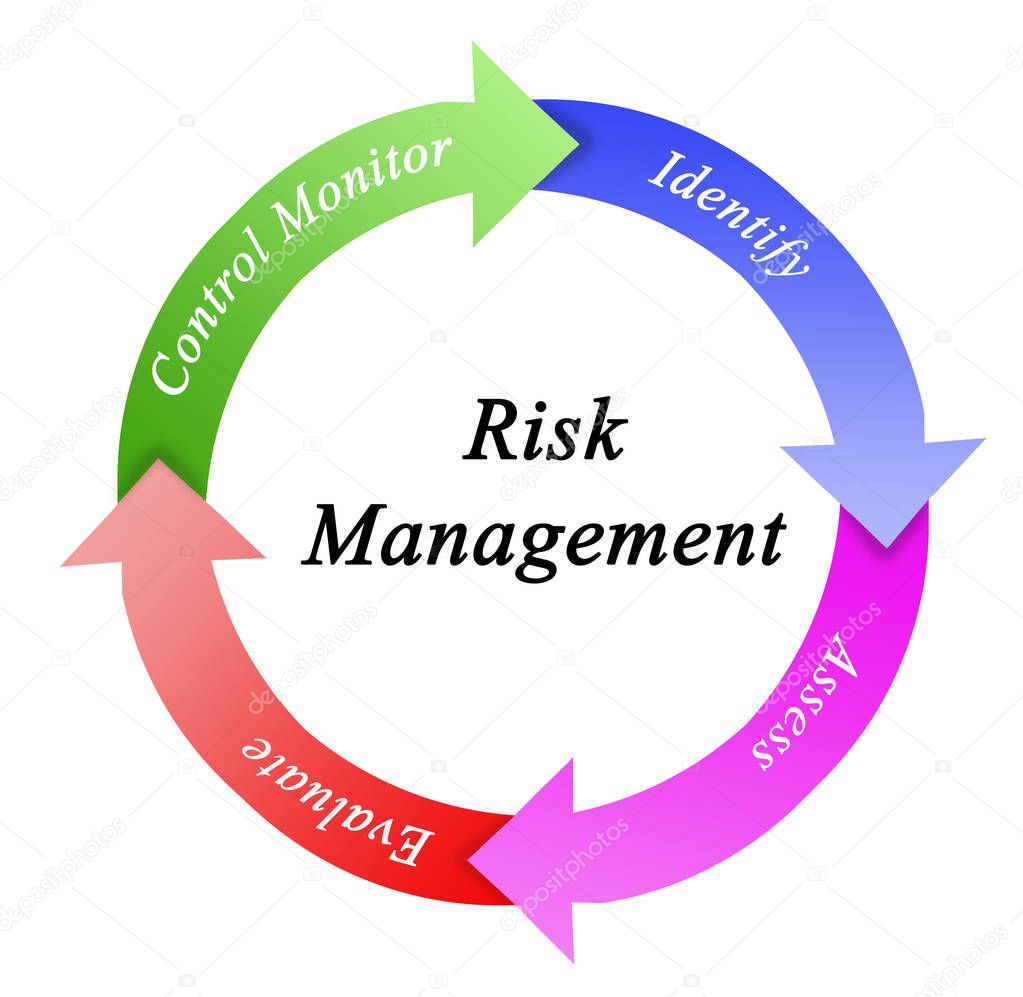
5.2 Risk Assessment
Risk assessment involves the following steps
5.3 Risk Assessment Frequency and Triggers
A routine risk assessment shall be performed on an annual basis covering Integra as a whole.
Non-routine risk assessments shall also be performed based on the following trigger events:
5.4 Building the Asset Inventory with Asset Values
a) Asset Identification
All assets in Integra will be identified for every department.
Assets will include information on paper, information in electronic media, devices that generate /hold / process / transmit information, and people information.
Assets will be designated at a grouped level that acts together to provide a particular function or serve similar utility. All ass ets will be listed in the “Asset Inventory,” identified with an asset identifier, location where available, its owner, custodian and its users.
b) Asset Categorization
Following guideline is adopted for categorizing / identifying the asset’s type / categorization for grouping similar assets:
c) Valuing the Assets
Following are the parameters considered for an asset’s valuation:
Confidentiality: The property that information is not made available or disclosed to unauthorized individuals, entities, or processes.
Integrity: The property of safeguarding the accuracy and completeness of assets.
Availability: The property of being accessible and usable upon demand by an authorized entity.
For computing the asset value, all the elements of the 3 parameters need to be taken into account, by giving some form of equal weightage.
Value of (C + I + A)
Hence, Asset Value = ------------------------------- rounded off to nearest 0.
3
The minimum value an asset can have is 1 and maximum asset value will be 3.
5.5 Risk Assessment and Risk Treatment Process
a) Identifying the “Threats”
The first step in carrying out a risk assessment is to identify the applicable threats to the asset. These will be the inherent risk that the asset will possess. The threat identification shall depend on the asset’s inherent physical property, its location within the facility, the operations where it is used in Integra, its dependence on technology and maybe other external factors.
b)Identifying the “Existing Preventive Measures”
Against each identified threat, there may be one or more preventive measures that are in place to counter the envisaged threat.
The existing preventive measures will demonstrate the extent of controls that is currently in place and help in realistically viewing the other vulnerabilities that the threat can exploit.
These existing preventive measures are basically the ISMS Controls that are in place.
c) Identifying the “Vulnerabilities”
Vulnerabilities are the weaknesses that could be exploited by a threat leading to a compromise of confidentiality, integrity and/or availability of an asset. Vulnerabilities are a factor of applicable threats and the existing controls in place to protect the asset. As part of this phase, existing and planned security controls should be identified to ensure that vulnerability assessment and risk treatment consider the current and planned controls.
d) The “Probability of Occurrence”
Determine the possibility of the weakness that can be exploited by a threat. Following probability
considerations may be given:
e) Identify the “Impact”
Determine the extent of damage that can happen should the threat materialize. The impact could
be on (but not limited to):
The higher the impact, the more concern it may be for the business managers.
f) The “Risk Value”
Risk is a function of asset’s value, the value of probability and the value of impact. Following algorithm will be applied to arrive at the measure of risk, viz,
Risk Value = Asset Value x Probability of Occurrence x Impact
The resulting risk value will be in a range of 1 as lowest and 27 as highest
Establish the “Chance of Detection”
Risks, particularly the high risks, need to be controlled. But every risk treatment needs to be balanced with a cost factor. Before the business managers embark on considering risks for treatment, the possibility of risk materializing and the ease of getting detected need to be considered, in order to prioritize the risk treatment.
Risk Priority Number (RPN)
This is an indicator for prioritization/ranking of risks that takes into account the risk value and its chance of detection. i.e.
RPN = Risk Value x Chance of Detection
In this risk assessment, the range of RPN is from 1 to 80. The range is exponential,
emphasizing the higher risks.
g) Determining Risk Treatment
Risks to an asset can be treated in one of the three ways:
Where none of the above can be applied, i.e., risks cannot be mitigated or avoided or transferred, or where the costs involved in treating the risk is higher than the asset’s business value, such risks shall be knowingly accepted, provided they clearly satisfy the organization’s procedure and criteria for risk acceptance.
Risk treatment procedures may follow the matrix described in Table-A below that represents a general guideline for risk treatment only. Business management should take appropriate decisions on risk treatment and/or risk acceptance
Table-A: Matrix for determining period for Risk Treatment / Mitigation
h)Preparing the Risk Treatment Plan
Information gathered during the risk assessment and the associated plan for risk treatment measures should be used as input in deciding Integra’s security strategy. A formal risk treatment plan should be prepared based on the priority of risks.
Following should be considered when preparing a risk treatment plan:
i) Residual Risk
After the risk treatment plan (RTP) is prepared, the residual risk is calculated. This is to determine the risk that will remain when the RTP will be done and will require a management approval prior to initiate implementing.
In order to compute the Residual Risk value, the new values after RTP for Probability, Impact, and Chance of Detection need to be determined.
Steps for computing residual risk:
In case the value of residual risk exceeds the acceptable risk levels after RTP implemented, the same may be taken up in subsequent risk assessment with management’s approval. Such decisions may be put up as a remark.
j) Risk Acceptable Criteria:
As per management guidance, risk acceptable limit shall be RPN 1 to 80. Such risk shall not require having initial treatment. However, due to implementation of best practices, initial control can be implemented. All other risk falls above RPN 20 shall be treated with appropriate mitigation controls.
There are few risks which are not having initial / final treatment to reduce risk under acceptable limit. In such case, management shall review the actual risk and its possible mitigation plan to be implemented. If no such mitigation plans available, management has rights to accept on it.